Configuring a Self-Signed Certificate
This procedure describes how to configure a self-signed certificate for HTTPs communication on Mac and Unix/Linux.
Use this procedure before configuring a Mac or Unix/Linux Agent to use SSL. (See Configuring a Mac Agent to use SSL.)
and Configuring a Unix Linux Agent to Use SSL
-
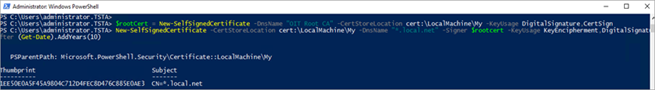
Open PowerShell as an Administrator and execute the following commands to create a root certificate and a site certificate.
-
Create a root certificate:
$rootCert = New-SelfSignedCertificate -DnsName "Your Company Name Dev Root CA" -CertStoreLocation cert:\LocalMachine\My -KeyUsage DigitalSignature,CertSign -
Create a site certificate:
New-SelfSignedCertificate -CertStoreLocation cert:\LocalMachine\My -DnsName "*.local.net" -Signer $rootcert -KeyUsage KeyEncipherment,DigitalSignature -NotAfter (Get-Date).AddYears(10)In the example:
DnsName for root certificate is
"OIT Root CA"DnsName for site certificate is
"*.local" -
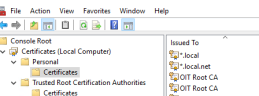
After you've created both certificates, run mmc.exe to open Microsoft Management Console (MMC).
-
From MMC, select File > Add/Move SnapIn to add the certificate.
-
Copy the created root certificate from the Personal Certifcate folder to the Trusted Root Certification Authorities > Certificates folder.
-
Assign the new self-signed certificate to ObserveIT Application Server.